Working with Control & Branch Process
Process Purpose
The "Control & Branch" process is used to check if a value/variable follows a given pattern. Depending on the result of this comparison ("True or False"), a destination point in the code (labels, routines, screens, etc.) will be defined.
When you add a process, you are required to define its settings. This occurs in the process's properties window which is displayed automatically after having added the "Control & Branch" process.
If any subsequent edition is required, double-click the process to open its properties window and enter the necessary modifications.

Fill in the options available:
If Value |
|
Value |
Define the value to compare. Either enter the value or click
|
Follows Pattern |
Define the other comparison element - a pattern- by entering it on the corresponding box. |
Action |
|
Then Go to |
Select a destination for a "True" result from the drop-down or the
|
Else Go to |
Select a destination from the drop-down or the
|
![]()
Pattern Syntax
The pattern is constructed/read one character at a time. These are the accepted characters:
* - ignores all characters -there is no pattern to perform a comparison (default).
0 -> 9
A -> Z
a -> z
? - Ignore/continue to the next character
@ - Decimal
$ - Any numeric character
" - Any alphabetic character
_ - Alphanumeric character
* - Ignore to end
> - Same as previous until
Use > to signify that from that point on, it must be of the type specified before.
$> all following characters are numeric.
_> all following characters are alphanumeric
Pattern Syntax Examples
01ZX"
The first character to be searched is 0, the second is 1, the third is Z, the fourth is X and the fifth is an unspecified alphabetic character.
The input will only be valid if it is 01ZX and an unspecified alphabetic character.
????$$$$
The first 4 characters are ignored and the following 4 characters must be numeric.
The input will only be valid if the fifth, sixth, seventh and eighth characters are numeric.
Detail of a ![]() window:
window:
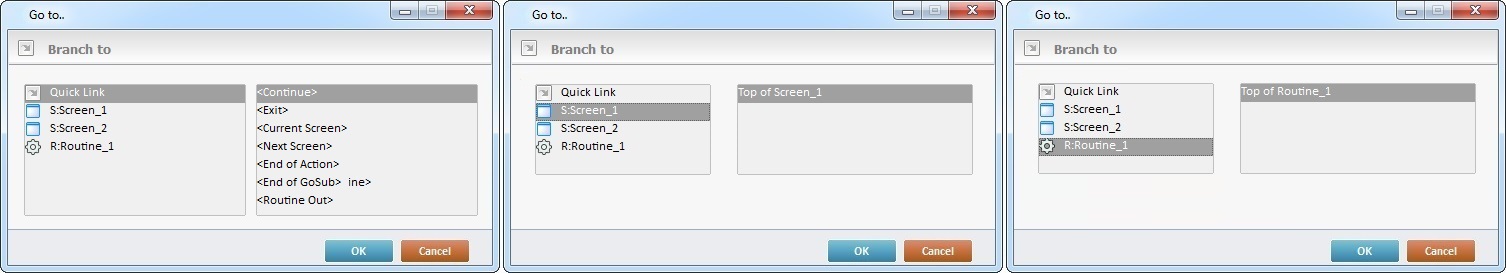
"S:Menu" is a screen included in the same program as the process.
"R:Routine_1" is a routine included in the same program as the process.
If required, use ![]() (on the upper right corner of the properties window) to attach any relevant notes to this process. Click it and enter your notes in the resulting text box. These notes will be displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window (in the "Notes" field) and in the "Developer Report".
(on the upper right corner of the properties window) to attach any relevant notes to this process. Click it and enter your notes in the resulting text box. These notes will be displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window (in the "Notes" field) and in the "Developer Report".
After filling in the required options, click ![]() to conclude or
to conclude or ![]() to abort the operation.
to abort the operation.
The added process is displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window.
![]() If you want to use a label as a target destination, you can use the "Auto-Label" mechanism. This alternative to the "Set Label" process allows you to create a label in the properties window of a process - specifically, in the fields used to define target destinations (ex: the "If Error..." type fields). See To Automatically Create a Label.
If you want to use a label as a target destination, you can use the "Auto-Label" mechanism. This alternative to the "Set Label" process allows you to create a label in the properties window of a process - specifically, in the fields used to define target destinations (ex: the "If Error..." type fields). See To Automatically Create a Label.
![]()
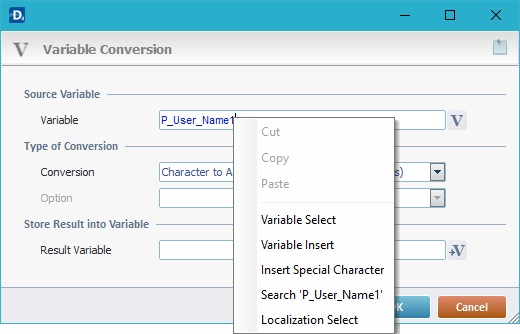
Use the right-click in MCL-Designer's input boxes to access some related options as well as the general "Cut", "Copy"; "Paste"; "Search" actions (active/inactive according to the current context).
Ex: If you right-click the "Variable" input box (included in a "Conversion's" properties window), you are provided with general editing/search actions and other more specific options such as "Variable Select" (see "Variable Select"); "Variable Insert" (see "Variable Insert"); "Insert Special Character" (see To Insert Special Characters into a Control's Text Input Field) and "Localization Select" (see Localization List).
If you right-click another input box, it may provide other possibilities.