Working with the NFC Processes Group
Process Purpose
NFC stands for Near-Field Communication (wireless) and its purpose is to detect and read information contained within NFC tags.
NFC tag detection operates within a radius of about 4 cm.
NFC technology is present mainly in Android devices.
This group of processes enables the use of NFC tag detection/data capture within an MCL application. See Example of "NFC Tag Reading" within an "MCL" Application.
![]() NFC related processes are ONLY applicable to Android devices with NFC technology.
NFC related processes are ONLY applicable to Android devices with NFC technology.
![]()
Make sure the NFC setting/feature is enabled in the target device's operating system.
The NFC Profile
The use of the NFC feature requires the setting of an NFC profile that defines what tags to read and/or which tag information to capture (ex: only capture the "MIME" information from the NFC tag). MCL-Designer provides a few standard profiles but it is possible to create and use customized NFC profiles with the appropriate settings (see To Create an NFC Profile below).
Standard Profiles
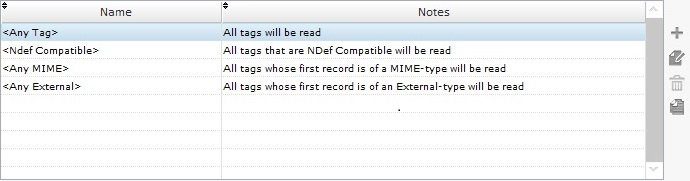
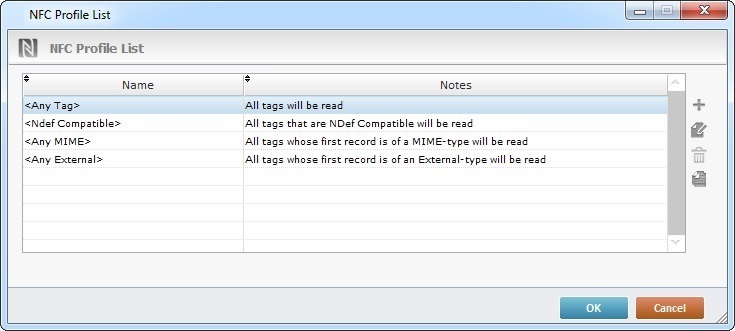
•Any Tag - this profile has no filters, it reads every tag that is detected.
•Ndef Compatible - Only reads the tags that are Ndef Compatible.
•Any MIME - Only reads tags with a first record containing MIME type information.
•Any external - Only reads tags with a first record containing External type information.
![]()
The standard profiles ("<Any Tag>", "<Ndef Compatible>", "<Any MIME>" and "<Any External>") are NOT editable.
Step-by-step
1. Use one of the following to open the table with the existing NFC profiles:
a. Open the "NFC/RFID" tab of the current project's properties window ("Project" menu ,in the Menu Bar > "Properties" option > "NFC/RFID" tab).
b. Click ![]() (whenever available).
(whenever available).
2. Double-click an empty row OR click ![]() (located to the right of the table).
(located to the right of the table).

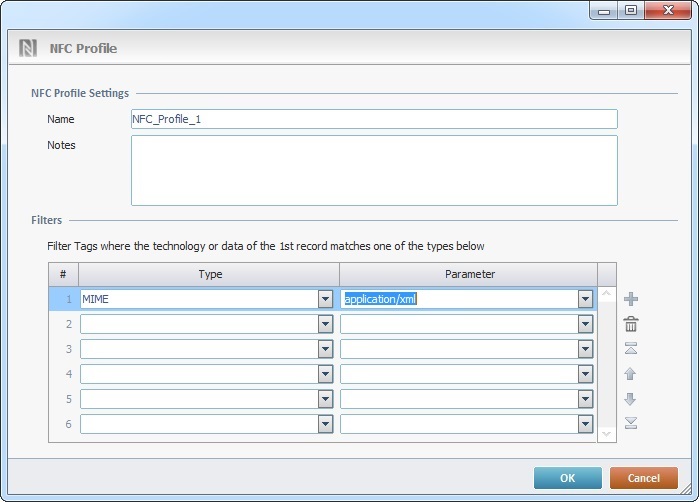
3. If required, rename the new profile (the default suggestion is "NFC_Profile_X") and/or add information on the new profile in the "Notes" box.
4. Define the necessary filters/parameters for the new NFC profile in the corresponding table fields.
a. In the "Type" column, select the type of information to be read from the NFC tag from the drop-down.
b. Associate a parameter to the "Type" filter - select the intended parameter in the corresponding "Parameter" drop-down.
![]() When defining filters/parameters for a customized NFC profile, take into account the NFC tag being used (the type of tag and its content).
When defining filters/parameters for a customized NFC profile, take into account the NFC tag being used (the type of tag and its content).
Use the editing icons to the right of the table to add,delete, copy and/or move the intended/selected row.
5. Click ![]() to conclude or
to conclude or ![]() to abort the operation.
to abort the operation.
| Click Here for an Example of "NFC Tag Reading" within an "MCL" Application |
This example illustrates how to develop an NFC Reading operation that only reads NFC tags of a specific type ("Technology" and/or "MIME") within an MCL application. Proceed as follows:
1. Create/select the screen where the NFC tag capture/read is supposed to take place.
2. Open the selected screen's Routine In and, in its "Routine" tab, add the "Enable NFC" process.
3. Open the selected screen and, in its "Actions" tab, select an "NFC" action.
4. We need to use a customized NFC profile to ensure that only tags with Technology and MIME type information are read so, click
5. Click
6. Rename the new profile as "My_NFC_Profile" and add the following filters/parameters in the corresponding table: Filter Type - Technology + Parameter - MifareUltralight Filter Type - MIME + Parameter - application/xml
7. Back in the screen's "Actions" tab, add the processes and corresponding settings described below. These processes ensure that when the application's workflow reaches the selected screen, the operator will be able to detect/read Technology/MIME type tags that contain specific information and only store the "text data" into the defined variable when record content "Type" has a specific value.
•The initial "Read NFC Record" process reads the detected tag's 1st record (since "Current Record" is set in the first process, the pointer is directed to the 1st record. In this case, it has the same effect as "First Record".) and stores the record's content into the "P_Type" program variable.
•The "Test & Branch" process is used to ensure the reading of a specific record content ("myapp.com:leasecar") - if the defined record includes this value, the workflow will continue to the next reading.
•The second "Read NFC Record" process reads the next tag record and stores the information in the "P_Model" program variable.
•The third "Read NFC Record" process reads the next tag record and stores the information in the "P_Plate" program variable.
|
This chapter covers the following topics:
----- Data |
----- Control |