Working with Read Process
Process Purpose
The "RFID Read" process is used in a "Single Tag” operation (synchronous operation) to read a tag's memory bank and store that information into variables.
![]() When reading more than 64 bytes of the User Memory Bank (for instance, the complete memory bank), the system will read the data in blocks of 64 bytes (RFID reader will flash multiple times).
When reading more than 64 bytes of the User Memory Bank (for instance, the complete memory bank), the system will read the data in blocks of 64 bytes (RFID reader will flash multiple times).
![]()
Make sure you have already created the required RFID profile(s). See Creating an RFID Profile.
Check the necessary steps to create an RFID program in To Create an RFID Program.
![]() The "RFID Read" process MUST NOT be associated to an "RFID" action.
The "RFID Read" process MUST NOT be associated to an "RFID" action.
When you add a process, you are required to define its settings. This occurs in the process's properties window which is displayed automatically after having added the "RFID Read" process.
If any subsequent edition is required, double-click the process to open its properties window and enter the necessary modifications.
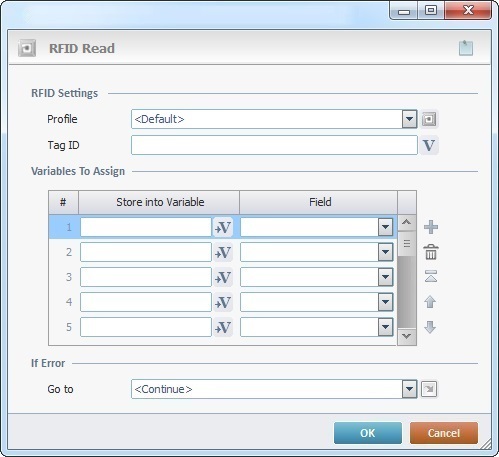
Fill in the following options:
RFID Settings |
|
Profile |
Select the appropriate RFID profile from the drop-down. If required, click |
Tag ID |
Define the tag to be read. Either enter the tag's ID OR click |
Variables to Assign |
|
Store into Variable column |
Click |
Field column |
Define the tag field to be read. Select the appropriate tag field from the drop-down. |
If Error |
|
Go to |
Select a target destination, in case an error occurs, from the drop-down or
|
Detail of a ![]() window:
window:
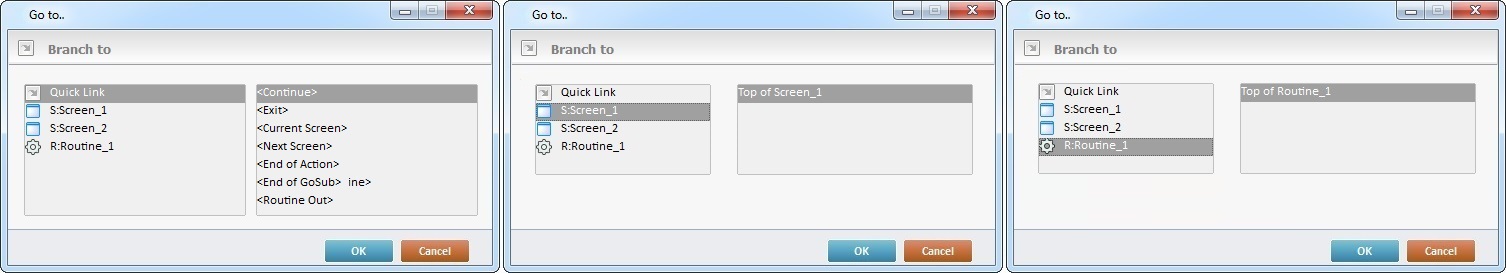
"S:Menu" is a screen included in the same program as the process.
"R:Routine_1" is a routine included in the same program as the process.
Use the editing icons to the right of the table to move the rows up and down and to delete or add more rows.
If required, click ![]() to attach any relevant notes to this process. Click it and enter your notes in the resulting text box. These notes will be displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window (in the "Notes" field) and in the "Developer Report".
to attach any relevant notes to this process. Click it and enter your notes in the resulting text box. These notes will be displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window (in the "Notes" field) and in the "Developer Report".
After filling in the required options, click ![]() to conclude or
to conclude or ![]() to abort the operation.
to abort the operation.
The added process is displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window.
![]() If you want to use a label as a target destination, you can use the "Auto-Label" mechanism. This alternative to the "Set Label" process allows you to create a label in the properties window of a process - specifically, in the fields used to define target destinations (ex: the "If Error..." type fields). See To Automatically Create a Label.
If you want to use a label as a target destination, you can use the "Auto-Label" mechanism. This alternative to the "Set Label" process allows you to create a label in the properties window of a process - specifically, in the fields used to define target destinations (ex: the "If Error..." type fields). See To Automatically Create a Label.
![]()
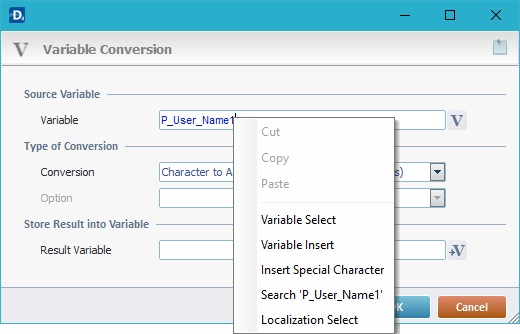
Use the right-click in MCL-Designer's input boxes to access some related options as well as the general "Cut", "Copy"; "Paste"; "Search" actions (active/inactive according to the current context).
Ex: If you right-click the "Variable" input box (included in a "Conversion's" properties window), you are provided with general editing/search actions and other more specific options such as "Variable Select" (see "Variable Select"); "Variable Insert" (see "Variable Insert"); "Insert Special Character" (see To Insert Special Characters into a Control's Text Input Field) and "Localization Select" (see Localization List).
If you right-click another input box, it may provide other possibilities.