Working with Print File Process
Process Purpose
The "Print File" process is used to request the printing of a file through WiFi, Ethernet, Bluetooth or serial ports. The file, usually, a "Print" type data file, can include:
•Fixed data (ex: a label format)
•Variable data (ex: a product code, quantity, price, image)
When MCL Local Variables are used inside the format of the label, they are replaced by their content when the device sends the file to the printer.
This process can be used with all portable printers that support an ASCII file.
When you add a process, you are required to define its settings. This occurs in the process's properties window which is displayed automatically after having added the "Print File" process. This properties window is divided into two tabs - "General" and "Advanced".
If any subsequent edition is required, double-click the process to open its properties window and enter the necessary modifications.
"General" tab
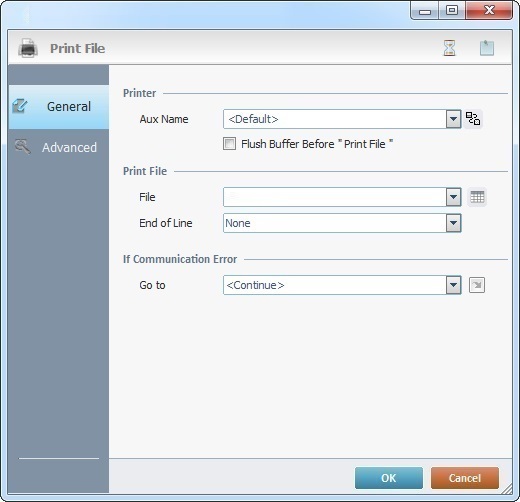
Fill in the available options:
Printer |
|
Aux Name |
Select the auxiliary device profile that will print the data from the drop-down. If required, click See To Create an Aux Profile and/or To Edit an Aux Profile.
Remember NOT to select a Serial Port Aux profile if your target device is an Android device. Serial Port type profiles are not supported if used in Android devices. |
Flush Buffer Before "Print File" |
Check this option to empty the device buffer before preparing and sending the file. |
Print File |
|
File |
Select the data file to be printed from the drop-down (see Print Files). If required, click |
End of Line |
Select the end of line character: None CR - (Carriage Return) Moves the cursor to the beginning of the same line. LF - (Line Feed) Moves the cursor to the next line, to the the same position. CR+LF - Moves the cursor to the beginning of the next line. |
If Communication Error |
|
Go to |
Select a target location from the drop-down or the
|
Detail of a ![]() window:
window:
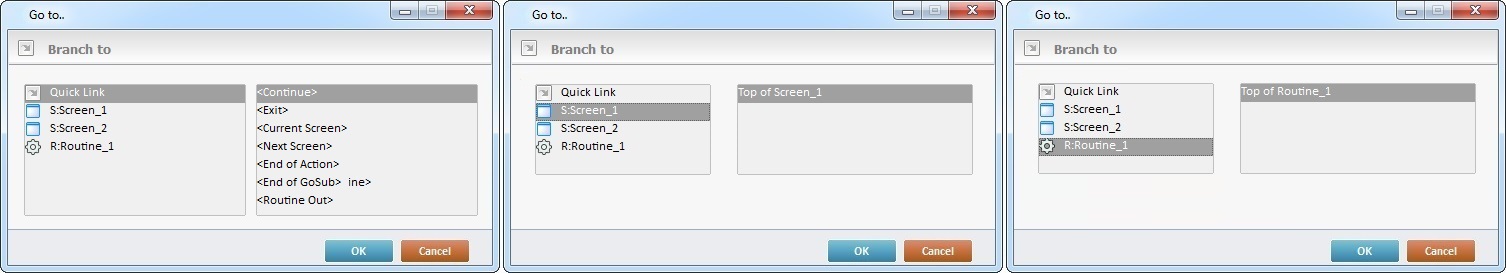
"S:Menu" is a screen included in the same program as the process.
"R:Routine_1" is a routine included in the same program as the process.
Go to the "Advanced" tab.
"Advanced" tab

Select/enter the appropriate information:
Standard Replacement |
|
Replace Variables |
Check this option to replace the variable tags by its values when the device sends the file to the printer. |
Replace Ascii |
Check this option to replace XX by the ASCII character when the device sends the file to the printer. |
Custom Replacement |
|
Replace Tags |
Check this option to define the replacement of custom tags. Custom tags must be defined in the content of the print file (label format). If checked, it activates the options below. |
Start Sequence |
Only active if the "Replace Tags" option is checked. Define the tag's start sequence (normally special characters such as @{ or $[). Enter it OR click |
End Sequence |
Only active if the "Replace Tags" option is checked. Define the tag's end sequence (normally special characters such as } or ]). Enter it OR click |
Tag to Replace column |
Only active if the "Replace Tags" option is checked. Select the tag ID or tag name to be replaced. Enter it OR click
|
Replacement Value column |
Only active if the "Replace Tags" option is checked. Enter the value that will replace the corresponding tag OR click |
Use the editing icons to the right of the table to move the rows up and down and to delete or add more rows.
Use the following recurring icons (located on the upper right corner of the properties window) to execute specific operations:
•Click ![]() to define a time out. See To Define a Time Out for a Print/Aux Process.
to define a time out. See To Define a Time Out for a Print/Aux Process.
•Click ![]() to attach any relevant notes to this process. Click it and enter your notes in the resulting text box. These notes will be displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window (in the "Notes" field) and in the "Developer Report".
to attach any relevant notes to this process. Click it and enter your notes in the resulting text box. These notes will be displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window (in the "Notes" field) and in the "Developer Report".
After filling in the required options, click ![]() to conclude or
to conclude or ![]() to abort the operation.
to abort the operation.
The added process is displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window.
![]() You can use relative paths to refer the file(s) you want to use in your project. See Working with Aliases.
You can use relative paths to refer the file(s) you want to use in your project. See Working with Aliases.
![]() If you want to use a label as a target destination, you can use the "Auto-Label" mechanism. This alternative to the "Set Label" process allows you to create a label in the properties window of a process - specifically, in the fields used to define target destinations (ex: the "If Error..." type fields). See To Automatically Create a Label.
If you want to use a label as a target destination, you can use the "Auto-Label" mechanism. This alternative to the "Set Label" process allows you to create a label in the properties window of a process - specifically, in the fields used to define target destinations (ex: the "If Error..." type fields). See To Automatically Create a Label.
![]()
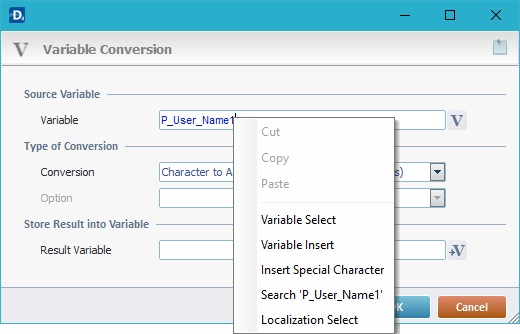
Use the right-click in MCL-Designer's input boxes to access some related options as well as the general "Cut", "Copy"; "Paste"; "Search" actions (active/inactive according to the current context).
Ex: If you right-click the "Variable" input box (included in a "Conversion's" properties window), you are provided with general editing/search actions and other more specific options such as "Variable Select" (see "Variable Select"); "Variable Insert" (see "Variable Insert"); "Insert Special Character" (see To Insert Special Characters into a Control's Text Input Field) and "Localization Select" (see Localization List).
If you right-click another input box, it may provide other possibilities.