Working with Parse Response Process
Process Purpose
The "Parse Response" process is used to parse a JSON or XML web service response into variables or into a file.
The web service response (body) to be parsed can be defined through an HTTP request included in the project (ex: a URL defined in the "Call & Parse" process) or you can retrieve the information from a variable, a data file or have it copied/pasted from an outside source.
You can parse up to 50 "path names" in one single process.
This process does not support responses with complex structures (multiple arrays).
When you add a process, you are required to define its settings. This occurs in the process's properties window which is displayed automatically after having added the "Parse Response" process. In this case, the properties window includes four tabs - "General", "Parse Simple", "Parse to File" and "Error".
If any subsequent edition is required, double-click the process to open its properties window and enter the necessary modifications.
"General" tab
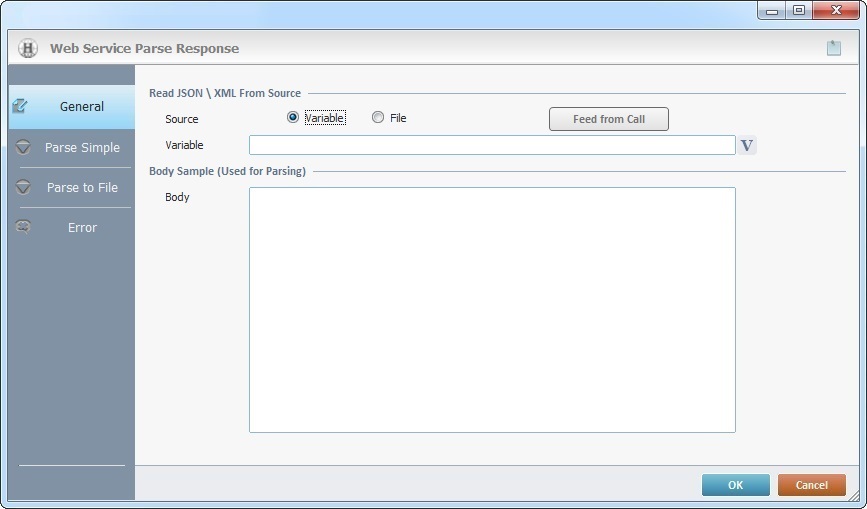
Fill in the following options:
Read JSON\XML From Source |
|||||||
Source |
Select the source of the JSON or XML response. The selection of the source (Variable/File) affects the related option (located below). If you do NOT want to use a variable or a file as a source, keep the box blank. |
||||||
Variable/File |
Depending on the selected source, you will access the corresponding field:
|
||||||
|
If you want to use the response of a web service being used within the project, click this button to automatically retrieve a list of the URLs being used in all "Call & Parse" process(es).
Use the |
||||||
Body Sample (Used for Parsing) |
|||||||
Body |
Displays the body of the response to be parsed. If the selected source for the response is a variable, a file or an available URL from the current project, this box will automatically display the corresponding response. As an alternative, you can dismiss the previous options and copy/paste a response body from an outside source into this box. Any performed edition, requires you clicking |
||||||
"Parse Simple" tab
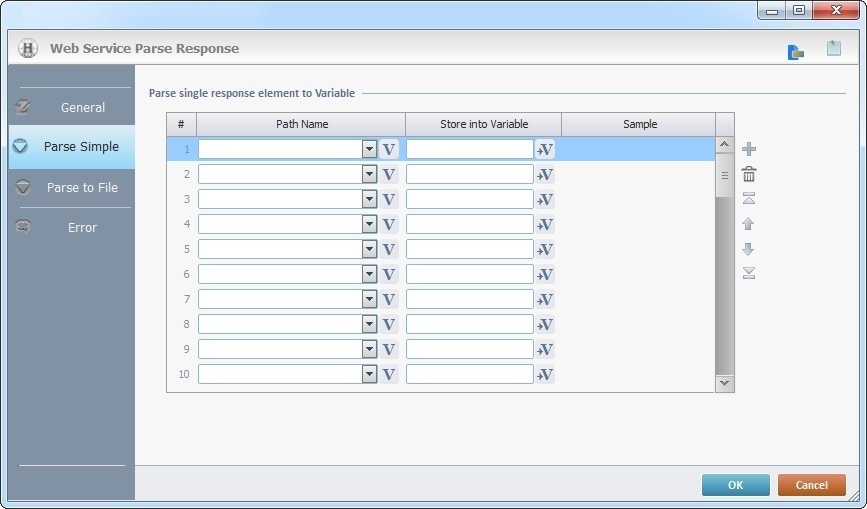
Fill in the following options:
Parse single response element to Variable |
|
Path Name column |
Define the response's elements you want to store into variables. Select the path name(s) from the drop-down OR click See The "Body to Use for Parsing" window. You can parse up to 50 "path names". |
Store into Variable column |
Click |
Sample column |
NOT editable. Displays a sample of the corresponding data (the selected path name). |
Use the editing icons to the right of the table to move the rows up and down and to delete or add more rows.
The ![]() button (that opens the "Test Web Service" window) is not available in this tab. It is replaced with the
button (that opens the "Test Web Service" window) is not available in this tab. It is replaced with the ![]() button which calls the "Body to Use for Parsing" window. This window focuses on the response's body and enables the drag-and-drop of the array/keys into the "Path Name" related fields. See The "Body to Use for Parsing" window.
button which calls the "Body to Use for Parsing" window. This window focuses on the response's body and enables the drag-and-drop of the array/keys into the "Path Name" related fields. See The "Body to Use for Parsing" window.
If you have opened the "Test Web Service" window (by clicking ![]() in the "Call" tab), and you proceeded to the "Parse Simple" or "Parse to File" tabs, it automatically switches to the "Body to Use for Parse" window
in the "Call" tab), and you proceeded to the "Parse Simple" or "Parse to File" tabs, it automatically switches to the "Body to Use for Parse" window

"Parse to File" tab
 .
.
Fill in the following options:
Parse list of elements (array) to Data File |
|
Target File Name |
Define the Target File Name from the drop-down. If you need to edit the selected data file, click |
Root Array |
Select the Root Array from the drop-down OR click |
From Path Name column |
Define the elements you want to store into data file fields. Select the Path Name(s) from the drop-down OR click If you have defined the root array with the use of the"Body to Use for Parsing" window, you may already have these fields filled in (the Drag-and-Drop of the array from the "Body to Use for Parsing" window allows for the automatic retrieval of the existing path names and the filling in of this column. |
To Field column |
Select the data file fields that will receive the information from the drop-down. |
Sample column |
NOT editable. Displays a sample of the corresponding data (the selected path name). |
Use the editing icons to the right of the table to move the rows up and down and to delete or add more rows.
![]()
When parsing the body of a JSON or XML response, do NOT create complex structures because they are not supported.
Simple Array (Recommended Structure) |
Multiple Arrays (Not Supported Structure) |
{ "Person": [ { "FirstName":<Data_Field_FirstName>, "LastName":<Data_Field_FirstName>, "Street":<Data_Field_Address_Street>, "Number":<Data_Field_Address_Number> } ] } |
{ "Person": [ { "FirstName":<Data_Field_FirstName>, "LastName":<Data_Field_FirstName>, "Address": { "Street":<Data_Field_Address_Street>, "Number":<Data_Field_Address_Number> "FirstName":<Data_Field_FirstName>, "LastName":<Data_Field_FirstName>, "Address": "Street":<Data_Field_Address_Street>, "Number":<Data_Field_Address_Number> { } } ] } |
Click![]() (located on the tab's upper right corner) to open the "Body to Use for Parsing" window. This is a useful window because you can view the web service response and use the Drag-and-Drop mechanism to define the displayed response's parsing in the related tabs. See The "Body to Use for Parsing" window.
(located on the tab's upper right corner) to open the "Body to Use for Parsing" window. This is a useful window because you can view the web service response and use the Drag-and-Drop mechanism to define the displayed response's parsing in the related tabs. See The "Body to Use for Parsing" window.
If you open a "Test Web Service" window (via the ![]() icon) in the "Call" tab and leave it open while proceeding to the "Parse to File" or "Parse Simple" tabs, the window will be replaced with the "Body to Use for Parsing" window.
icon) in the "Call" tab and leave it open while proceeding to the "Parse to File" or "Parse Simple" tabs, the window will be replaced with the "Body to Use for Parsing" window.
"Error" tab
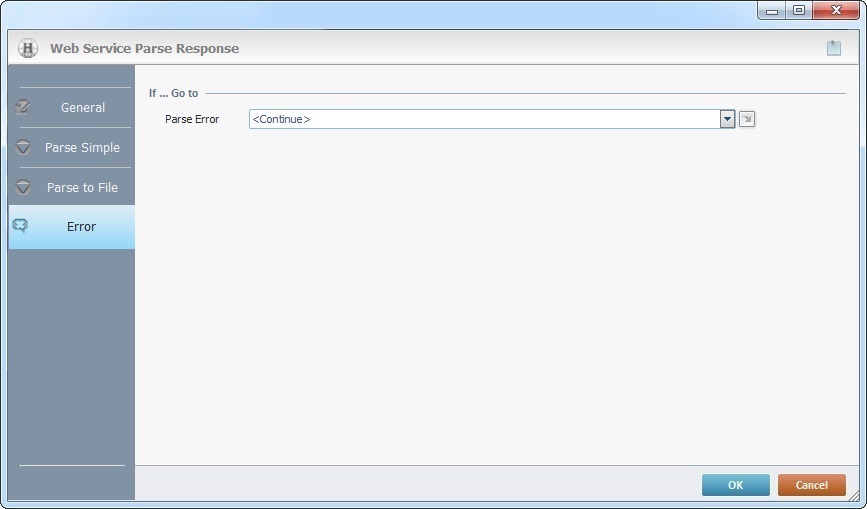
Fill in the following options:
If ... Go to |
|
Parse Error |
Select a target location from the drop-down or
|
Detail of a ![]() window:
window:
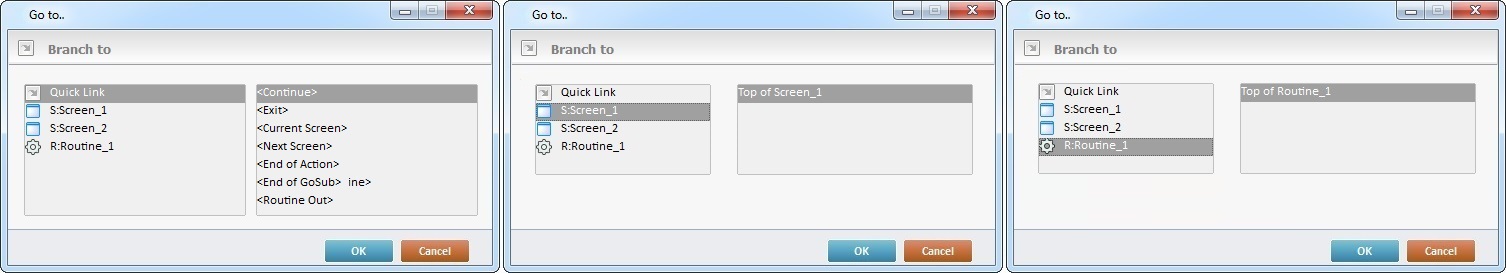
"S:Menu" is a screen included in the same program as the process.
"R:Routine_1" is a routine included in the same program as the process.
If required, click ![]() (on the upper right corner) and enter info about this process in the resulting text box. These notes will be displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window (in the "Notes" field) and in the "Developer Report".
(on the upper right corner) and enter info about this process in the resulting text box. These notes will be displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window (in the "Notes" field) and in the "Developer Report".
When you are done filling in/editing the tabs of the properties window, click ![]() to apply.
to apply.
The added process is displayed in the corresponding "Actions" tab or "Process" window.
The "Test Web Service" window (called from the "Web Service Call" window)
The "Web Service Call" window (accessed via the ![]() button) includes the access to a "Test Web Service" window concerning the selected URL. It allows you to test the URL, view the corresponding response information and to manipulate the data (ex: defining path names via the "Body to Use for Parsing" window and the Drag-and-Drop mechanism).
button) includes the access to a "Test Web Service" window concerning the selected URL. It allows you to test the URL, view the corresponding response information and to manipulate the data (ex: defining path names via the "Body to Use for Parsing" window and the Drag-and-Drop mechanism).
Step-by-step
1. Select the URL that prompted the response you intend to parse.

2. Click ![]() to open the "Test Web Service" window with the response.
to open the "Test Web Service" window with the response.
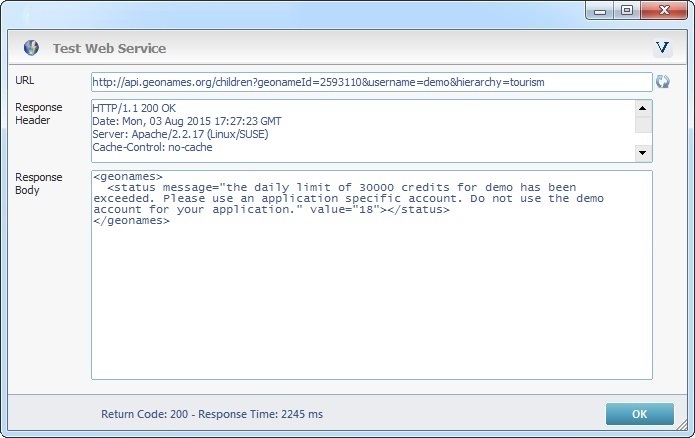
3. If required, edit the window's content with the use of the right-click options or keyboard keys and click ![]() to save those changes.
to save those changes.
![]()
Use this window's editing capabilities, if you want to parse different responses from the same web service.
4. Click ![]() if you want to refresh the web service's information.
if you want to refresh the web service's information.
5. If the web service's response includes variables, use the ![]() icon to define a value for each variable. See Detail of a Set Variable Values window.
icon to define a value for each variable. See Detail of a Set Variable Values window.
6. Once you are done, click ![]() to close it and return to the "Web Service Call" window.
to close it and return to the "Web Service Call" window.
![]() If you want to use a label as a target destination, you can use the "Auto-Label" mechanism. This alternative to the "Set Label" process allows you to create a label in the properties window of a process - specifically, in the fields used to define target destinations (ex: the "If Error..." type fields). See To Automatically Create a Label.
If you want to use a label as a target destination, you can use the "Auto-Label" mechanism. This alternative to the "Set Label" process allows you to create a label in the properties window of a process - specifically, in the fields used to define target destinations (ex: the "If Error..." type fields). See To Automatically Create a Label.
![]()
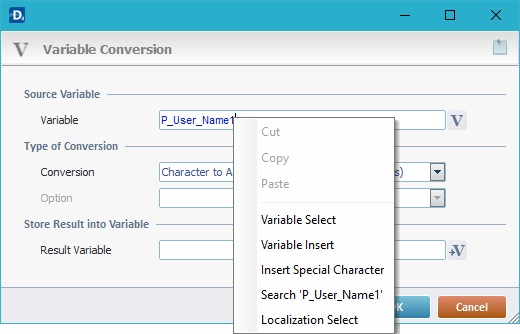
Use the right-click in MCL-Designer's input boxes to access some related options as well as the general "Cut", "Copy"; "Paste"; "Search" actions (active/inactive according to the current context).
Ex: If you right-click the "Variable" input box (included in a "Conversion's" properties window), you are provided with general editing/search actions and other more specific options such as "Variable Select" (see "Variable Select"); "Variable Insert" (see "Variable Insert"); "Insert Special Character" (see To Insert Special Characters into a Control's Text Input Field) and "Localization Select" (see Localization List).
If you right-click another input box, it may provide other possibilities.